Has this article been insightful? Share it!
Though the phrase ‘peripheral nerve disorders’ may sound obscure, many individuals experience them. For instance, the persistent ache you feel on your wrist after typing on a keyboard for an extended period of time is known as carpel tunnel syndrome, a form of peripheral nerve disorder with a 10% lifetime risk.
Nerves are bundles of fibres that run throughout the body. Their primary function is to transfer information from one area of the body to another using electrochemical impulses. These nerves can be classified into three types: sensory, motor, and autonomic. They enable movement and aid in the perception of various sensations such as heat, touch and pressure.
Peripheral nerve disorders are defined as nerve damage in the body’s extremities, which include the hands, feet, and arms. This can lead to pain or lack of sensation for touch, temperature and position sense, as well as motor weakness. This has a significant impact on the patient’s overall quality of life.
Risk factors such as trauma, viral infections, hereditary conditions, and metabolic disorders like diabetes or hypothyroidism can all contribute to peripheral neuropathy diseases. The most common causes of peripheral nerve disorders include traumatic injuries, entrapment neuropathies and metabolic conditions.
Although there are many types of peripheral nerve disorders, the more common ones include:
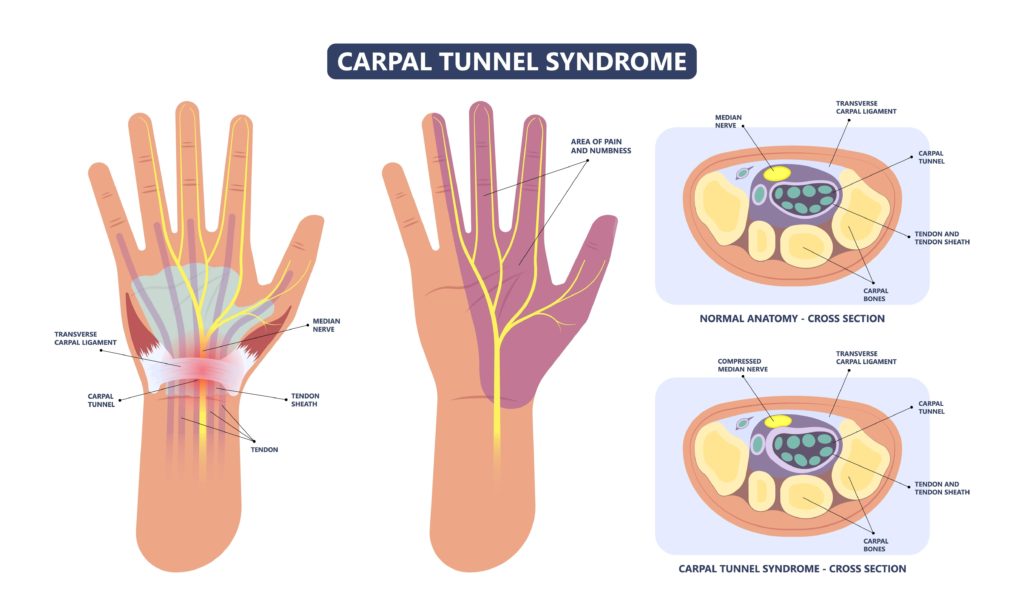
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a peripheral nerve disorder that occurs when the nerves in the carpal tunnel (which is a limited space) of the wrist are compressed. Then, the median nerve swells, leading to irritations and pain in the fingers and forearm, especially at night.
If the nerve sustains significant damage, the patient may experience a loss of sensation in their thumb, index, and middle fingers. Thereafter, the patient will develop muscle weakness that will prevent them from using these fingers.
Carpal tunnel syndrome can be caused by repetitive nerve compression due to vibrating equipment use, wrist-crushing injuries, and ligament inflammation in the carpal tunnel.
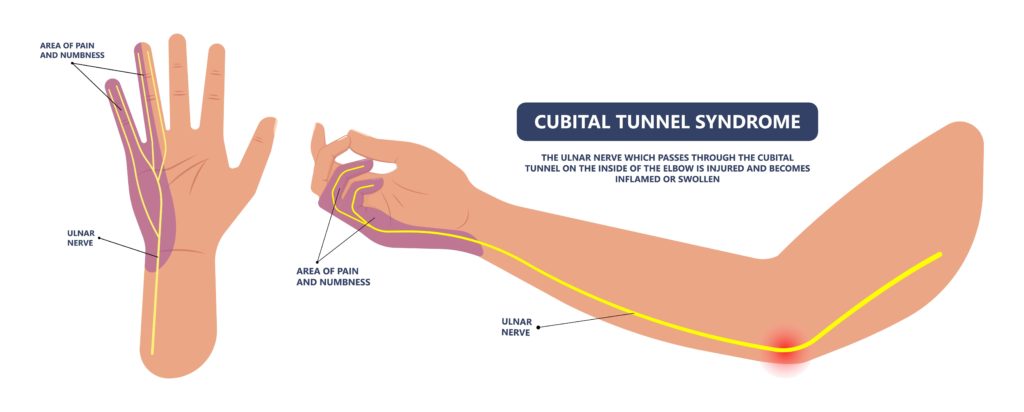
Ulnar nerve entrapment, also known as cubital tunnel syndrome, is a disorder which affects the ulnar nerve that extends from the neck all the way down to the wrist. It is typically caused by prolonged stretching of the ulnar nerve and occurs at the wrist or within the elbow.
One of the main causes of ulnar nerve entrapment is the prolonged application of pressure to your elbows and wrists, such as when you lean your elbows on a solid surface or on your bike handlebars for extended periods of time.
Symptoms of peripheral nerve disorders include:
If you notice unusual tingling sensations, weakness or pain in your hands and feet, you should consult a neurosurgeon. Keep in mind that early diagnosis leads to early treatment, which improves your chances of managing the condition and preventing further damage.
There are several causes for peripheral nerve disorders. Some of these are:
You can expect your doctor to take a full medical history and a neurologic test that examines the following:
Your neurosurgeon may also order some additional tests to aid in their diagnosis. These tests may include blood tests, thyroid function tests, nerve biopsies, nerve conduction tests as well as electromyography.
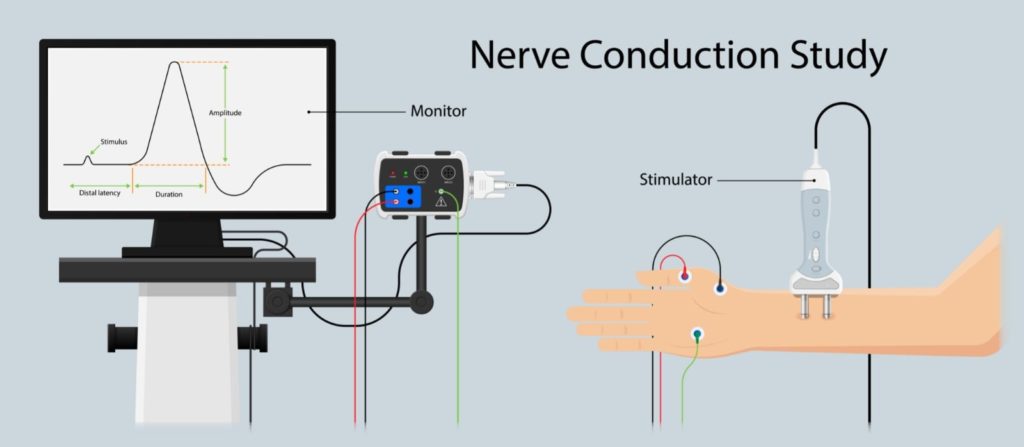
Peripheral nerve disorders are typically diagnosed through a series of tests such as:
NCS can identify any damage to your nerves by measuring how quickly an electrical impulse moves through your nerves. During the test, two electrode patches will be pasted onto your skin. One of the electrode patches stimulates the nerve by sending a mild electrical impulse while the other records it. This process is repeated with every nerve that is being evaluated.
EMG helps to detect muscle abnormalities by measuring the muscles’ reaction or electrical activity in response to a nerve’s stimulation of the muscle. Small needles known as electrodes are poked through the skin into the muscles. Any electrical activity will be detected and amplified. EMG will measure the electrical activities of muscles during rest, as well as slight contractions and forceful contractions. As such, you may be asked to bend or lift your arm or leg during an EMG test. An EMG test is typically performed immediately after an NCS test.
A nerve biopsy involves extracting a sample of nerve tissue to examine nerve fibre endings for damage.
Radio imaging, such as MRI and CT scans, can help identify any nerve compressions, herniated disks or vascular issues that may affect nerves.
There is a wide array of methods used to treat peripheral nerve disorders. Some of them include:
Medications
Medications such as nortriptyline and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors may be prescribed to help ease the pain.
Open surgery
Open surgery is the more commonly used method and involves cutting a wider area in order to access the affected nerve. It is often associated with longer recovery times and more pain.
Along with causing unnecessary pain, peripheral nerve disorders can disrupt a patient’s quality of life. Therefore, it is critical that you recognise these symptoms and seek expert care as soon as possible to prevent them from worsening. To schedule a consultation, get in touch with us today!
Contact Us For More Information
We provide quality specialised care for neuro and spine conditions.
For enquiries, leave a message and our friendly team will get in touch with you.
Monday – Friday: 9:00AM – 5:00PM
Saturday: 9:00AM – 12:30PM
Sunday & Public Holiday: Closed
We provide quality specialised care for neuro and spine conditions.
For enquiries, leave a message and our friendly team will get in touch with you.
Monday – Friday: 9:00AM – 5:00PM
Saturday: 9:00AM – 12:30PM
Sunday & Public Holiday: Closed
We provide quality specialised care for neuro and spine conditions.
For enquiries, leave a message and our friendly team will get in
touch with you.
Monday – Friday: 9AM – 1PM | 2PM – 5PM
Weekends & Public Holidays: CLOSED
© 2023 All Rights Reserved | Advanced Brain & Spine Surgical Centre | Terms & Conditions